
This document (http://www.WORDesign.com/systemsdesign) is submitted to James Lowe, UC Berkeley Extension Instructor, in partial fulfillment of the Spring 1998 course on Systems Analysis and Design: An Overview (X422)
| Introduction |
| Proposed System Overview |
| Alternative I: PharmaForms™ |
| Alternative II: Data Fax |
| Comparison |
| Summary |
| References |
The Biomedical field is booming, and Tools (databases and software to analyze a biomedical problem) rank number one (over medical devices, heath care services, diagnostics, and therapeutics) for biomedical venture capital funding. We--Daniel Leprince, Preeti Tikekar, Fan Shen, Vijay Patel, Krishna Shroff, and Thomas Albert--therefore establish Berkeley Medical Systems™ to satisfy with state-of-the-art software (PharmaForms™ for "digital reliability in clinical trials"™), hardware, and networking technologies the critical demand for accelerated time-to-market of new pharmaceutical therapies that address such terminal ailments as malignant cancer tumors.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a regulatory agency within the United States Department of Heath and Human Services, oversees the process by which a pharmaceutical company (drug therapy sponsor) brings a new medication to market. The journey from laboratory discovery to routine prescription can take over 15 years and cost up to three hundred million dollars. "Each one day delay in a 12-year testing cycle can cost the sponsor more than $1 million."
Our solution, PharmaForms™, address the Clinical Research phase.
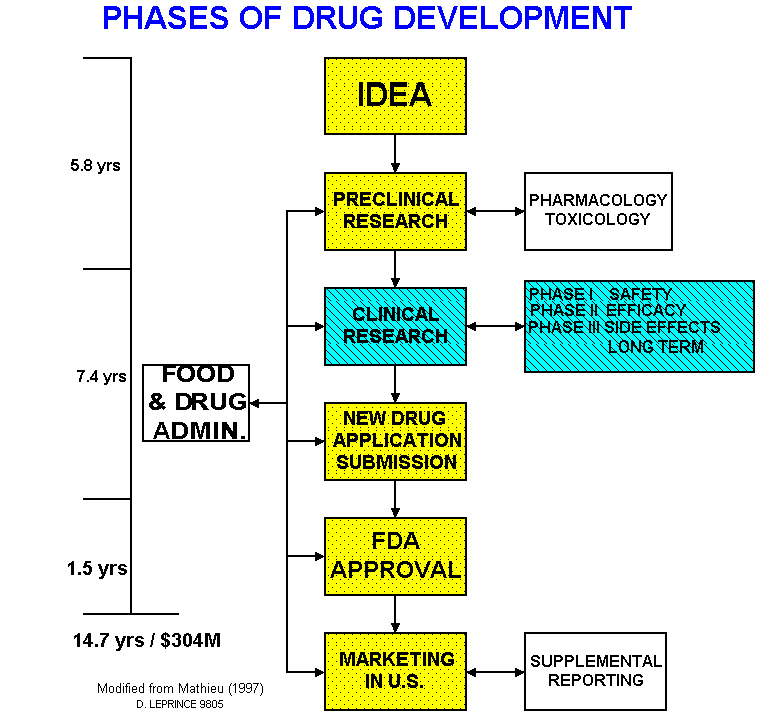
PHASES OF DRUG DEVELOPMENT
Afterwards,
- Phase I study tests the safety of the compound at recommended doses
- Phase II tests efficacy of the drug as a cure or therapy
- Phase III study measures short- and long-term side effects
- still requires the sponsor to monitor any adverse medical events for as long as the drug is marketed
- still subject to FDA review
Berkeley Medical Systems PharmaForms are a proposed solution to the high cost, frequent errors, and unnecessary delays in the clinical process. Accelerating the time to market of critical drug can mean dozens of saved or improved lives, as well as revenue to the sponsor of up to one million dollars per day. This proposal follows FDA Guidelines for electronic forms in clinical research.
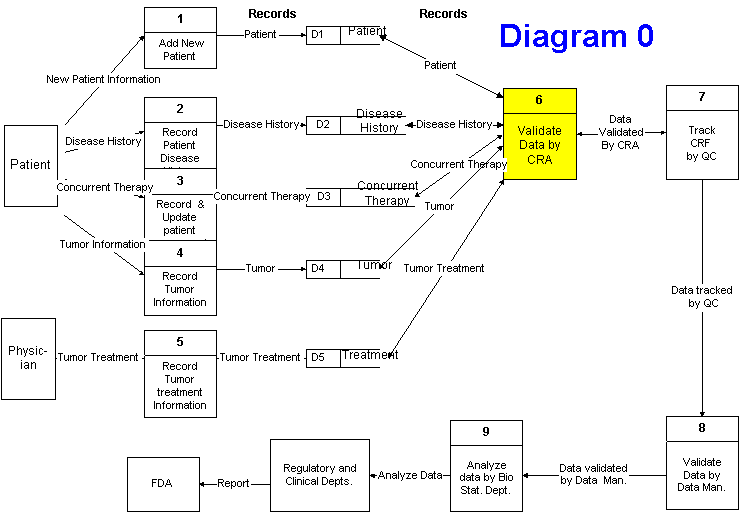
1. Add new patient
The sponsor (the pharmaceutical company) relies on doctors or a contract research
organization (CRO) to recruit patients willing to undergo the study. Recruiting subjects
for clinical trials is itself a costly and time-consuming tasks. Terminally ill patients
who do not foresee recovery with traditional therapies sometimes agree to participate as
subjects in a clinical trial with hopes of gaining better health, a longer life, or at
least contributing to medical progress. For the sponsor, more participants strengthens the
evidence and the likelihood that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepts the
study's findings. Typical studies can have from 100 to 9000 patients. Studies often a
placebo (an inert pill) to a control group in a "blind label" experiment.
Patient who received placebo later have the option of taking the proposed drug in an
"open label" experiment.
An example of a contract research organization is the Sagar Group (http://www.sagargroup.com).
2. Record patient disease history
Typically, the doctor takes the history, but the doctor can authenticate a history that
originates with a nurse or Clinical Research Assistant.
3. Record and update concurrent therapy
Often, patients are taking drugs other than the one under study. Recording concurrent
therapies allows the study to
4. Record tumor information
This is a prime area for human error, especially in busy, if not hectic, hospital
settings. Our proposed PharmaForm solution automates the calculation of tumor size and
body size
5. Clinical Research Associate (CRA) validates data
The CRA validates data by going through patients' files and making certain that
investigators are following regulations and research
protocols. Sometimes the CRA encounters missing, erroneous, or "out-of-range"
data. In these cases, the CRA has to spent time and money to obtain correct information.
Each day delay in the testing cycle can cost a top-selling drug company one million
dollars in lost revenue ("Oracle
Clinical Helps Get New Drugs to Market", Oracle Magazine, April 1998, p.
76). Three days can be lost if CRA must fly to the original hospital--which could be in
any country in the world-- physically locate the nurse or doctor there who entered
erroneous data (or failed to enter required data), create a paper trail of study
modifications, and send via overnight FedEx the correction to study headquarters.
6. Quality Control (QA) tracks CRF (Clinical Report Form)
The Quality Control specialist
7. Data Management validates data and performs quality
control screening
The data management department
8. BioStat (biological statistics) analyzes data
Programmers and statisticians analyze data according to study protocols and report using
analysis tables and data
listings. Statistical analyses enable the sponsor to state findings about the safety and
efficacy of the new drug with a specific level of confidence. The strength of the
statistical evidence often determines FDA approval.
9. Regulatory and Clinical report to FDA
10. FDA approves, responds with issues, or audits the study
FDA evaluation board
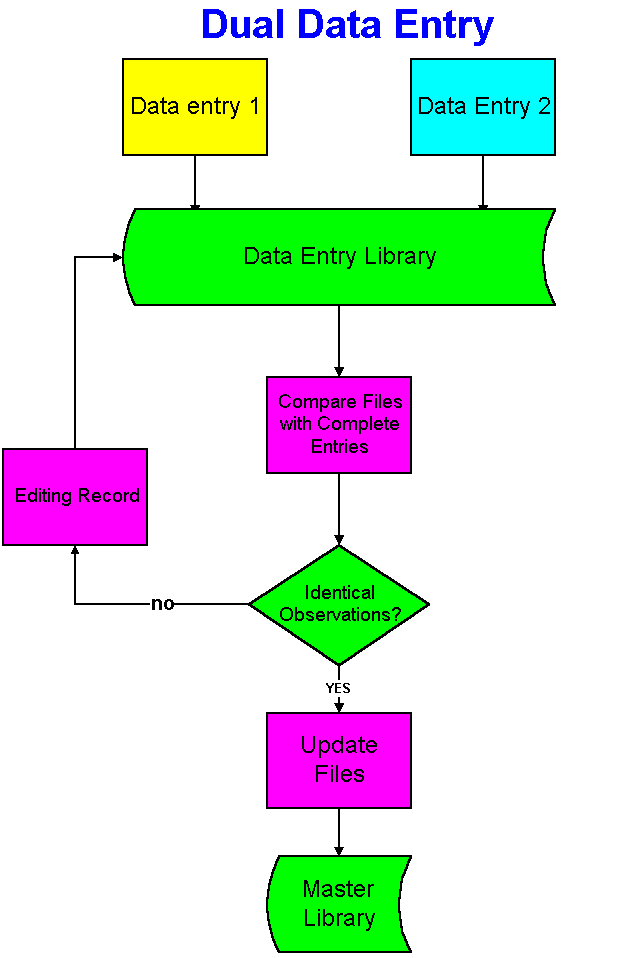
Dual data entry is a process to insure homogeneity between the data recorded on the form and the one transferred in the database. The underlying principle is that two different persons are unlikely to make the same mistake in data entry, and that reconciliation of differences is the best way to ensure integrity and accuracy between the data on Case Report Forms (CRFs) and the data stored in the database. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry with Case Report Forms. Two clerks are entering the same CRF information in a data entry library through two data entry screens. A validation program compare data entry 1 to data entry 2. If the observations are identical this information is loaded in the master library, otherwise, the records in the data entry library are edited and the validation program is run again. This process is repeated until all differences are accounted for. One of the benefits of using electronic forms is the elimination of dual data entry because data integrity and completeness is enforced automatically.
 Problems with Current System
Problems with Current System
Berkeley Medical Systems gathered and analyzed information from a wide variety of sources:
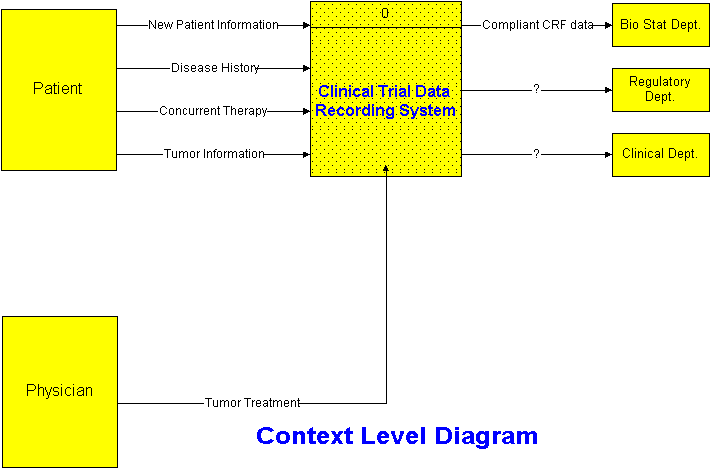
PharmaForms are designed to integrate well with the physician’s daily routine, and ease the tedium of reporting on patients and treatments. Most cancer specialists have an isolated cubicle where they do paperwork and make phone calls. These cubicles are ideal for establishing internet connections.
How Departments Work Together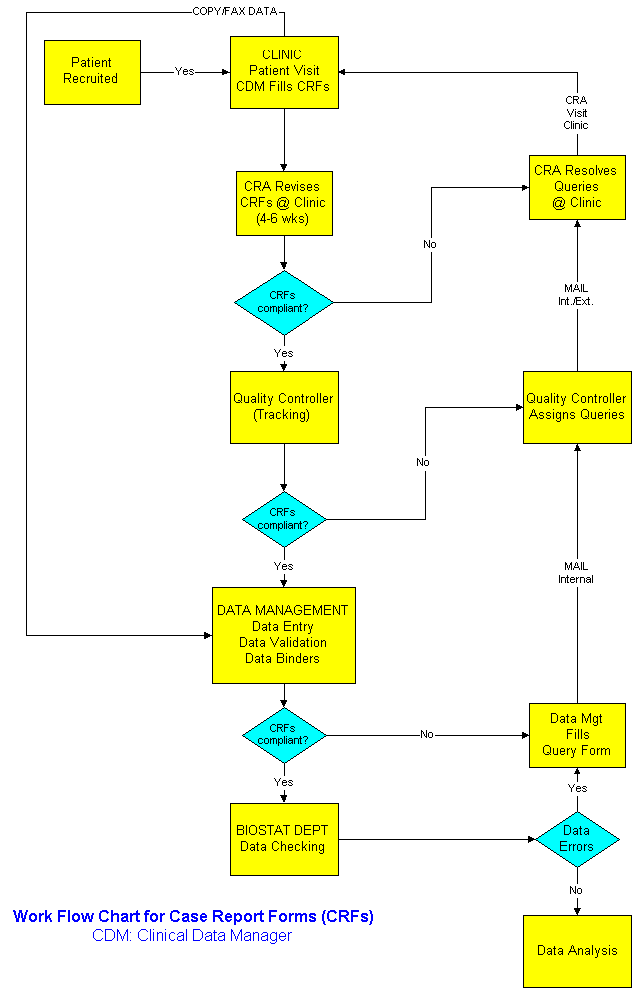
Berkeley Medical Systems™ designed the PharmaForm™ database with a data dictionary customized with tables and many-to-one relations that manage clinical data collection and verification.
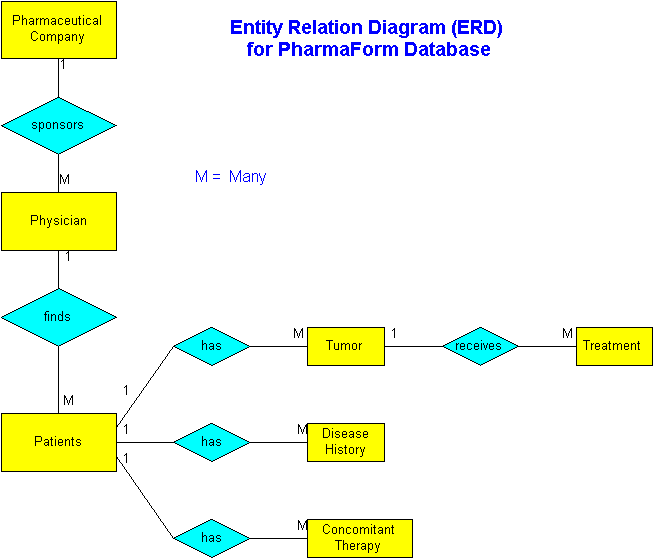
Data Type: N = Numeric, A = Alphanumeric, D = Date MM/DD/YY
| Data Item | Data Item Description | Data Type | Data Length |
| INVID | Investigator Identification | A | 4 |
| INVLNAME | Investigator Last Name | A | 20 |
| INVMNAME | Investigator Middle Name | A | 20 |
| INVFNAME | Investigator First Name | A | 20 |
| INVSTADD | Investigator Street Address | A | 30 |
| INVCITY | Investigator City | A | 20 |
| INVSTATE | Investigator State | A | 2 |
| INVZCODE | Investigator Zip Code | N | 9 |
| INVPHONE | Investigator Phone Number | N | 9 |
| PATID | Patient Identification | A | 4 |
| PATLNAME | Patient Last Name | A | 20 |
| PATMNAME | Patient Middle Name | A | 20 |
| PATFNAME | Patient First Name | A | 20 |
| PATSTADD | Patient Street Address | A | 30 |
| PATCITY | Patient City | A | 20 |
| PATSTATE | Patient State | A | 2 |
| PATZCODE | Patient Zip Code | N | 9 |
| PATPHONE | Patient Phone Number | N | 9 |
| PATBIRTH | Patient Birthday | D | 8 |
| PATSEX | Patient Sex | N | 8 |
| PATRACE | Patient Ethnicity | N | 8 |
| PATWEIGH | Patient Weight | N | 8 |
| PATHEIGH | Patient Height | N | 8 |
| TUMORID | Tumor Identification | A | 5 |
| TUMORLEN | Tumor Length | N | 8 |
| TUMORWEI | Tumor Width | N | 8 |
| TUMORHEI | Tumor Height | N | 8 |
| VISITID | Visit Identification | A | 4 |
| VISITDAY | Visit Date | D | 8 |
| PROTOID | Protocol Identification | A | 11 |
| DSASVLSN | Dose Assigned Volume Per Tumor | N | 8 |
| DSDSVLSN | Dose Destroyed Volume Per Tumor | N | 8 |
| DOSERSNC | Dose Discrepancy Reason Code | N | 8 |
| DOSERSND | Dose Discrepancy Reason Description | A | 50 |
| PRISUR ID | Prior Surgery Procedure Identification | A | 4 |
| PRISURDS | Prior Surgery Procedure Description | A | 50 |
| PRISURDA | Prior Surgery Date | D | 8 |
| CONMED ID | Concomitant Medication ID | A | 4 |
| CONMEDDE | Concomitant Medication Description | A | 60 |
| CONMEDIN | Concomitant Medication Indication | A | 120 |
| CONMEDDU | Concomitant Medication Dose Unit | N | 8 |
| CONMEDFQ | Concomitant Medication Frequency | A | 20 |
| CONMEDSD | Concomitant Medication Start Date | D | 8 |
| CONMEDED | Concomitant Medication End Date | D | 8 |
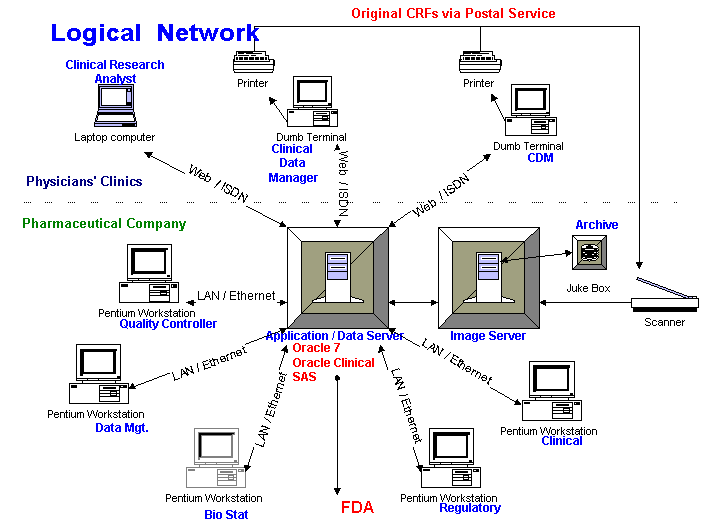
Application/Data Server for users:
Image Server:
Programming Cost for the Forms |
$40/hr for two months |
$13,866.00 |
||
SAS License |
? |
? |
||
Sub Total |
$130,621.00 |
|||
GRAND TOTAL |
$283,166.00 |
To reduce costs, we recommend dumb terminals, rather than fully equipped personal computers, at the beginning of the project. We assume that the sponsor’s U.S. and Canadian clinics are or can be connected to the internet. Dumb terminals support the critical needs: identifying the patient and visit; downloading forms for data entry.
The sponsor provides hardware to North American clinics having several patients. The data is stored on a central server that enforces data integrity and security. Standard reports answer Frequently Asked Questions by investigators and send the results to the clinics. Database personnel respond to special requests from investigators.
Encryption and Data Security
After evaluating two competing products, Defensor and Entrust, we chose Entrust, the simplest solution with the least training for clients. The Entrust ® public-key infrastructure (PKI) software provide adequate yet affordable security through encryption for the sensitive information relating to PharmaForms™. Entrust key management is automatic and transparent to the user. This solution is fully scalable for our future needs.Information about Entrust users is securely archived in the Entrust/Manager database. Entrust/Manager also acts as the Certification Authority (CA), issuing all X.509 public-key certificates. The main functions of Entrust/Manager include:
All security-related events that occur in Entrust/Manager are recorded in audit trails. These records are time-stamped and contain information such as the identity of the person causing the event. This provides integrity control as the audit log files are protected and cannot be manipulated without detection.
This directory contains the name of each person in the organization and acts as a repository for public-key certificates. Administrator’s are responsible for creating a directory entry for each Entrust user. Entrust uses this entry to store the user’s encryption public-key certificate in the Directory.
Entrust/Admin is the main administrative interface to the Entrust system and is used by Security Officers, Administrators, and Directory dministrators. It can be accessed securely over a network or on the workstation that hosts Entrust/Manager.
Entrust/Client allows users to encrypt and digitally sign files decrypt files and verify digital signatures create signing key pairs receive key updates on a regular basis validate certificates before encrypting files for other users or when verifying digital signatures on files securely delete files.
These functions are accessed through an easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI) that makes key management transparent. Entrust/Client also provides other valuable features, such as the ability to manage frequently used lists of recipients, and the option to save disk space and manage potected files with file compression and archiving.
PharmaForms™ Clinical Intelligence™We built Clinical Intelligence™ into PharmaForms™ to minimize the possibility of human error
To enforce data integrity we employ
We designed electronic case report forms using Visual Basic and incorporated formulas that faciliate data entry and significantly reduce the possibility of human error.
For example, the New Patient Screening form
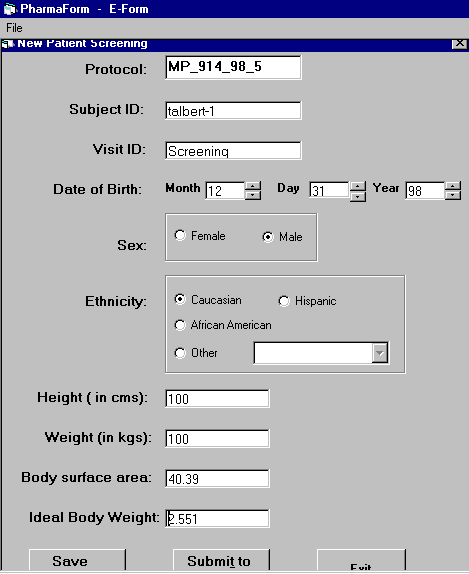
(10%), values unreadable (4.5%), values outside acceptable range (2%), and others (4.5%).
E-CRF eliminates 41.2% of the queries problems in the first wave by capturing
and associating these with the appropriate record.
For auditing, each original or modified record would be automatically associated with
Other data entry errors are eliminated:
71% of all queries could be avoided with the use of E-CRF
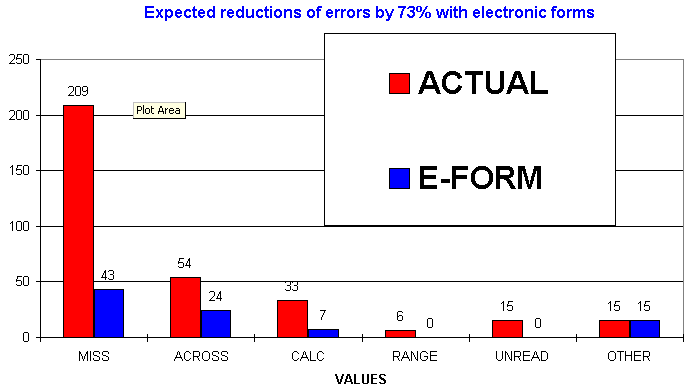
In a second wave of improvement with E-CRF, visual and audible warnings associated with missing required fields prompt the user attention to populated them. We estimate a 70% reduction of missed fields.
In a third wave of improvements, beyond the scope of this presentation, comparisons of values across forms and visits are dramatically reduced through database querying before uploading the forms.
Calculations of Costs associated with the current procedure
Based on our interview with the manager of Data Management, it takes one hour on average
for a clerical employee to file a query that need to be sent to the field (i.e. filing
query, copying forms on a different color, writing questions and sending). These queries
are generally resolved by Clinical Research Assistant when he or she visits the clinics
every 4-6 weeks. Excluding travel expenses, one hour of work is associated with each
query. Two packages being sent by express mail for each query bring the cost of each query
to $55: $40.00 of labor plus $15.00 of shipping costs. This conservative estimate excludes
the costs of the time spent by physicians, study coordinators at the clinical site,
quality controller, and double data reentry.)
The reduction of 71% of the queries (n=939) to the field save the sponsor $28,400 for an indication of 65 patients. Since several indications are being pursued simultaneously by the sponsor, we anticipate a similar proportion of savings in other studies.
Hardware for Alternative I |
|||||||
Category |
Specifications |
Unit Price |
Quantity |
Total Price |
|||
Server |
Ultra SPRC II 250 NHz Work Station, |
10,000 |
1 |
10,000 |
|||
1 MB Cache with built-in 10/100 Ethernet, |
|||||||
3.1 GB Hard Drive, 16x CDROM, |
|||||||
HP Tape Drive, 15" SVGA Monitor, |
|||||||
SUN Solaris 2.6 Desktop Liocense |
|||||||
Exceed X Server with 5 licenses, |
|||||||
Novell Server with 5-licenses, Ethernet Cards |
|||||||
with Hub |
|||||||
Desktop Machines |
Compaq Intel 166 Mhz Pentium Processor |
$1,399.00 |
4 |
5,596 |
|||
w/MMX Technology, 32 MB SDRAM |
|||||||
1 GIG Ultra ATA Hard Drive/20x CDROM |
|||||||
15" Viewsonic |
|||||||
56 K US Robotics Modems |
|||||||
Microsoft Windows 95/Office97 |
|||||||
Business Addition |
|||||||
LaserJet Printer |
Hewlett Packard Laserjet 6Lse Printer |
$399.00 |
2 |
$800 |
|||
SOFTWARE |
|||||||
Category |
Specifications |
Unit Price |
Quantity |
Total Price |
|||
DataFax Licenses |
4-user DataFax software license1 |
5 |
117,000 |
||||
Desktop Publishing |
Adobe Frame Maker 5.5 |
$800 |
1 |
$800 |
|||
Grand Total ($) |
134,196 |
||||||
NOTE: |
|||||||
1. First Year License Fee. Annual renewal fee is $48,000/year. |
|||||||
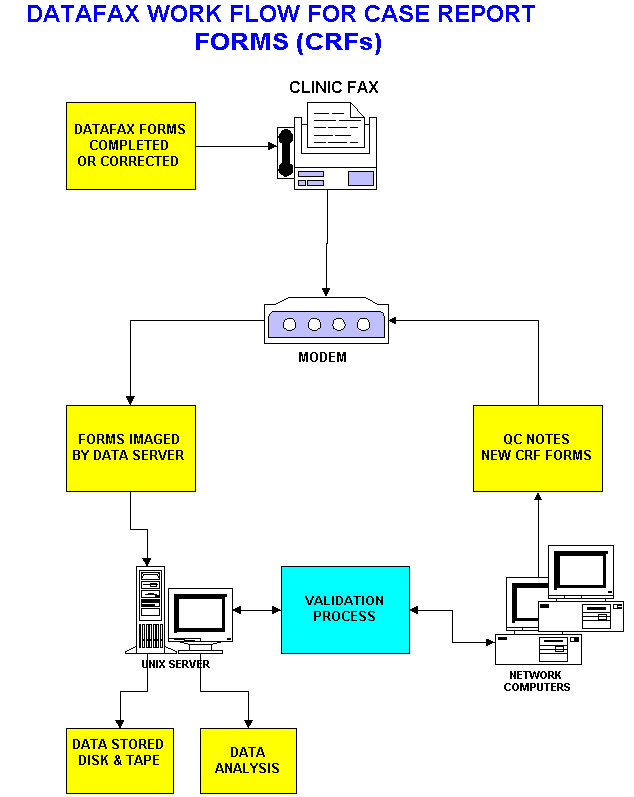
DataFax is a data management system designed to manage paper data forms which are faxed from remote sites to a central computer running the DATAFAX system. DataFax is used by organizations to collect and process patient data from hospitals and clinics participating in clinical research studies.
DATAFAX Features:
Platforms: Hardware and Operating Systems
Hardware for Alternative II |
|||||||
Category |
Specifications |
Unit Price |
Quantity |
Total Price |
|||
Server |
Ultra SPRC II 250 NHz Work Station, |
10,000 |
1 |
10,000 |
|||
1 MB Cache with built-in 10/100 Ethernet, |
|||||||
3.1 GB Hard Drive, 16x CDROM, |
|||||||
HP Tape Drive, 15" SVGA Monitor, |
|||||||
SUN Solaris 2.6 Desktop Liocense |
|||||||
Exceed X Server with 5 licenses, |
|||||||
Novell Server with 5-licenses, Ethernet Cards |
|||||||
with Hub |
|||||||
Desktop Machines |
Compaq Intel 166 Mhz Pentium Processor |
$1,399.00 |
4 |
5,596 |
|||
w/MMX Technology, 32 MB SDRAM |
|||||||
1 GIG Ultra ATA Hard Drive/20x CDROM |
|||||||
15" Viewsonic |
|||||||
56 K US Robotics Modems |
|||||||
Microsoft Windows 95/Office97 |
|||||||
Business Addition |
|||||||
LaserJet Printer |
Hewlett Packard Laserjet 6Lse Printer |
$399.00 |
2 |
$800 |
|||
SOFTWARE |
|||||||
Category |
Specifications |
Unit Price |
Quantity |
Total Price |
|||
DataFax Licenses |
4-user DataFax software license1 |
5 |
117,000 |
||||
Desktop Publishing |
Adobe Frame Maker 5.5 |
$800 |
1 |
$800 |
|||
Grand Total ($) |
134,196 |
||||||
NOTE: |
|||||||
1. First Year License Fee. Annual renewal fee is $48,000/year. |
|||||||
Alternative II is a less bold step that would attract clinical management operating in a conservative mode. Alternative I offers larger benefits of time/money economy in the mid- to long-run, but does require greater effort up front. Since very little of the gains expected in Alternative II would carry over to a later migration to Alternative I, and since competitors can opt for a route similar to Alternative I, we recommend the organization commit adequate resources for Alternative I. Moreover, Alternative I inherent scalability, and the guaranteed reduction of paper, serve organizational goals as pharmaceutical sponsors add greater numbers of larger projects.
We have explained the current process of data management in clinical trials, and seen how two alternative systems address, to varying degrees, shortcomings inherent in paper-intensive traditional (or legacy) operations. We believe the design we show provides a detailed feasibility study, and subject to management approval, should prove itself in initial prototyping and usability tests as warranted for the attainment of organizational goals.
| $532 million in 1997 in Silicon Valley alone ("Expertise Critical in Daring Field of Biotech Investing", Scott Herhold, San Jose Mercury News, Sunday, May 17, 1998, pp. 1D., 4D. |
| "NTC: Oracle Clinical Helps Get New Drugs to
Market", Oracle Magazine, March/April 1998, p. 76., and Information Technology for Management: Improving Quality and Products, Efraim Turban, Ephraim McLean and James Wetherbe (New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1996), p. 19. |
| "Guidance for Industry: Computerized Systems Used in Clinical Trials", draft of June 18, 1997, U.S. Department of Heath and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. |
| http://www.datafax.com - provides fax (rather than digital data) solutions for forms |
| http://www.oracle.com - provides back end databases as well as the Oracle Clinical application for managing aspects of clinical studies |
| http://www.sas.com - provides powerful statistical analysis solutions |
| http://www.sagargroup.com - a contract research organization and information technology provider |
| New Drug Development: A Regulatory Overview, 4th ed., M. Mathieu (Parexel, 1997) |
| Systems Analysis and Design, 3rd ed., Kenneth E. Kendall and Julie E. Kendall (New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1995). |
You are visitor number: