
| 22 April 2002
This lecture covers the reading in Day 11: Responding to User Input |
So that your class can respond to user events, such as mouse clicks, you
implement event listeners, which the java.awt.event package provides as
interfaces such as the following.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/package-summary.html
| Interface Summary | Example | |
| ActionListener | The listener interface for receiving action events. | mouse click |
| AdjustmentListener | The listener interface for receiving adjustment events. | scrollbar moved by user clicking the bar or its arrows |
| ComponentListener | The listener interface for receiving component events. | |
| ContainerListener | The listener interface for receiving container events. | |
| FocusListener | The listener interface for receiving keyboard focus events on a component. | text field gets focus; loses focus [focus means currently active for input] |
| InputMethodListener | The listener interface for receiving input method events. | |
| ItemListener | The listener interface for receiving item events. | check box changed |
| KeyListener | The listener interface for receiving keyboard events. | keystrokes |
| MouseListener | The listener interface for receiving "interesting" mouse events on a component. | press, release, click, enter, and exit |
| MouseMotionListener | The listener interface for receiving mouse motion events on a component. | |
| TextListener | The listener interface for receiving text events. | |
| WindowListener | The listener interface for receiving window events. | maximize, minimize, move, close |
In the following sample,

Line 31 implements the actionPerformed() method of the ActionListener
interface:
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/ActionListener.html
The listener interface for receiving action events. The class that is
interested in processing an action event implements this interface, and the
object created with that class is registered with a component, using the
component's addActionListener method. When the action event occurs,
that object's actionPerformed method is invoked.
The code above handles action events on JButtons. You also use the actionPerformed() method for other components: JCheckBox, JComboBox, JTextField, and JRadioButton.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/ActionEvent.html

An action event object inherits the getSource() method from the EventObject class. Therefore, line 32 can use the getSource() method of the action event instance evt to determine the cause (source) of the user's action.
How do you make a scroll bar that adjusts itself in response to the user?

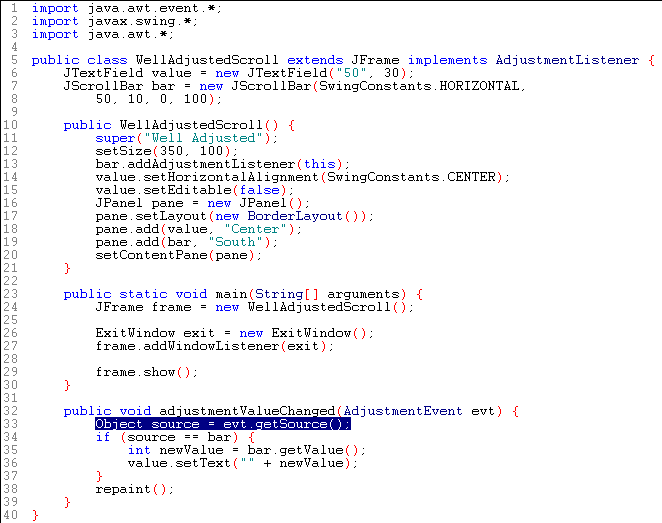
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/components/scrollpane.html
Example of an application that adjusts the size of the scroll pane to fit
whatever the drawing area displays.
Line 36 uses a null string ("") as a shortcut to convert the newValue integer into a string.
A text field has the focus when it is active for user input. Typically, the cursor blinks in the text field with focus.
Like the ActionListener, the FocusListener is a subinterface of the
EventListener interface.
Just as you can call getSource() on an action event, so you can call getSource
on a focus event.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/FocusListener.html
void |
focusGained(FocusEvent e)Invoked when a component gains the keyboard focus. |
void |
focusLost(FocusEvent e)Invoked when a component loses the keyboard focus. |
How you make the GUI respond to the user selecting an item from a pick list?


http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/KeyEventDemo.html
This applet displays as text whatever key event you cause.
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/keylistener.html
Description of the key event listener, including this code to handle
keyboard events:

The MouseListener interface provides five methods.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4/docs/api/java/awt/event/MouseListener.html
| Method Summary | |
void |
mouseClicked(MouseEvent e)Invoked when the mouse button has been clicked (pressed and released) on a component. |
void |
mouseEntered(MouseEvent e)Invoked when the mouse enters a component. |
void |
mouseExited(MouseEvent e)Invoked when the mouse exits a component. |
void |
mousePressed(MouseEvent e)Invoked when a mouse button has been pressed on a component. |
void |
mouseReleased(MouseEvent e)Invoked when a mouse button has been released on a component. |
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/MouseEventDemo.html
The applet above responds to the user's mouse events by display descriptive
text.
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/mouselistener.html
Here is the code to handle mouse events.
 .
.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4/docs/api/java/awt/event/MouseMotionListener.html
void |
mouseDragged(MouseEvent e)Invoked when a mouse button is pressed on a component and then dragged. |
void |
mouseMoved(MouseEvent e)Invoked when the mouse button has been moved on a component (with no buttons down). |
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/WindowListener.html
| Method Summary | |
void |
windowActivated(WindowEvent e)Invoked when the window is set to be the user's active window, which means the window (or one of its subcomponents) will receive keyboard events. |
void |
windowClosed(WindowEvent e)Invoked when a window has been closed as the result of calling dispose on the window. |
void |
windowClosing(WindowEvent e)Invoked when the user attempts to close the window from the window's system menu. [You could prevent the window from closing!] |
void |
windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e)Invoked when a window is no longer the user's active window, which means that keyboard events will no longer be delivered to the window or its subcomponents. |
void |
windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e)Invoked when a window is changed from a minimized to a normal state. |
void |
windowIconified(WindowEvent e)Invoked when a window is changed from a normal to a minimized state. |
void |
windowOpened(WindowEvent e)Invoked the first time a window is made visible. |
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/WindowEventDemo.html

http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/events/windowlistener.html

![]()
Line 45 uses the getWindow method of the WindowEvent class.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/event/WindowEvent.html#getWindow()

The SwingColorTest application has three panels:
![]()
The constructor defines the layout manager (line 13), sets the controls, and adds the controls to the pane.

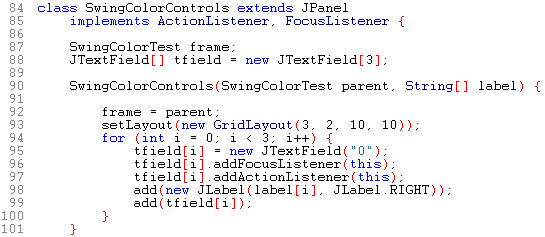
Line 88 creates an array for the text fields.
Lines 94-100 use a for loop to add each text field in the array.
Before you begin writing code for the logic of HOW the GUI works, you should first verify that the GUI has the correct LOOK, that all the necessary components are in the proper place.

The workflow is as follows:
The update() method tests which column is the source of the update:

To handle the conversion from RGB to HSB, use the RGBtoHSB() method of the Color class.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/Color.html#RGBtoHSB(int,
int, int, float[])
public static float[] RGBtoHSB(int r,
int g,
int b,
float[] hsbvals)

Line 65 casts the floats in the HSB array to integers so that the valueOf() method of the String class can convert the values to strings.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/awt/Color.html#getHSBColor(float, float, float)
public static Color
getHSBColor(float h,
float s,
float b)
Color object based on the specified values for the
HSB color model.
The example includes three classes:



______________
course
homepage course
calendar